Precision Targeting Of TFAP-2
Initiative #1
Explore Our Project
Research Question
The effectiveness of treatments – chemotherapy, surgery, drugs are hindered by the development of TME resistance mechanisms.
The research question is if we can create a more personalized and effective treatment to tumor metastasis and provide an accessible, affordable, and sustainable melanoma treatment via addressing tumor heterogeneity by manipulating the features of tumors themselves.
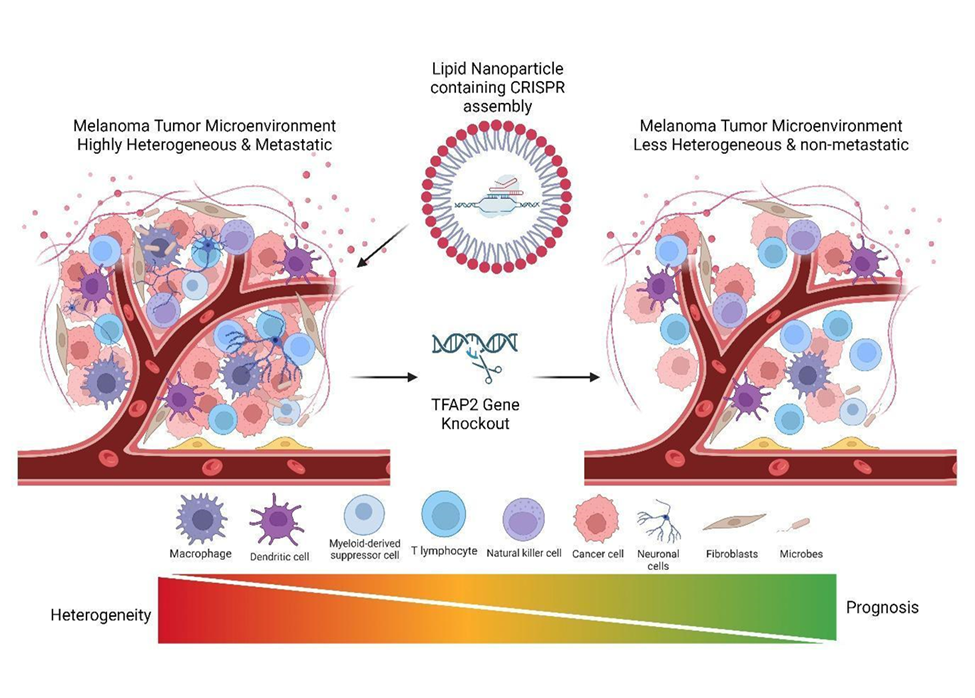
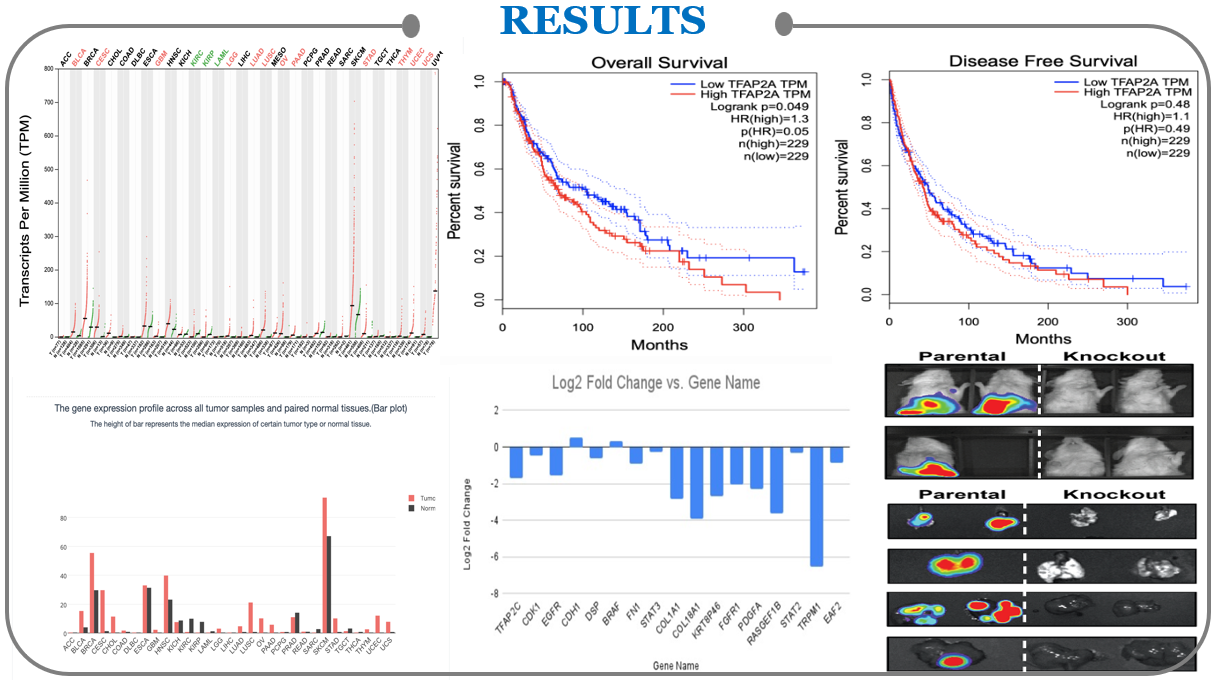
Hypothesis is that TFAP2 is important in targeting melanoma and subsequent alteration of tumor microenvironment which can be achieved by reducing innervations and extracellular matrix sensing of melanoma cells. This analysis has focused on the TFAP2 isoform TFAP2A, which has been found to be overexpressed in melanoma and is associated with poor overall and disease-free survival in patients to offer a pathway targeting TFAP2 in melanoma cells via a CRISPR/Cas9 pathway and emphasizes the use of LNPs as a safe and precise delivery mechanism for in vivo gene editing.
Abstract
Cancer is a complex and multifaceted disease that has plagued humanity for centuries characterized by the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells that can invade and destroy healthy tissues (1). Melanoma, also known as malignant melanoma, is a type of skin cancer that develops from pigment-producing cells known as melanocytes. Melanoma’s impact spans beyond the skin, affecting various body areas like the eyes, scalp, and even nails. Melanoma poses a formidable challenge to healthcare professionals worldwide due to its aggressive nature and resistance to conventional treatments. Surgical tumor removal is standard care while targeted therapy and immunotherapy has drastically increased the survival chances. These therapies along with conventional chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and small molecule inhibitors are inefficient as tumor relapse is very common in melanoma patients. This project envisions addressing the gap in the therapeutic landscape for melanoma due to the inefficacy of these therapies. To address this challenge, this research offers a computational approach in quantifying the targeting of TFAP2 in melanoma cells. Transcription Factor AP-2 (TFAP2) is a group of related proteins that regulate genes that help control cell division and the self-destruction of cells that is no longer needed.
Analysis
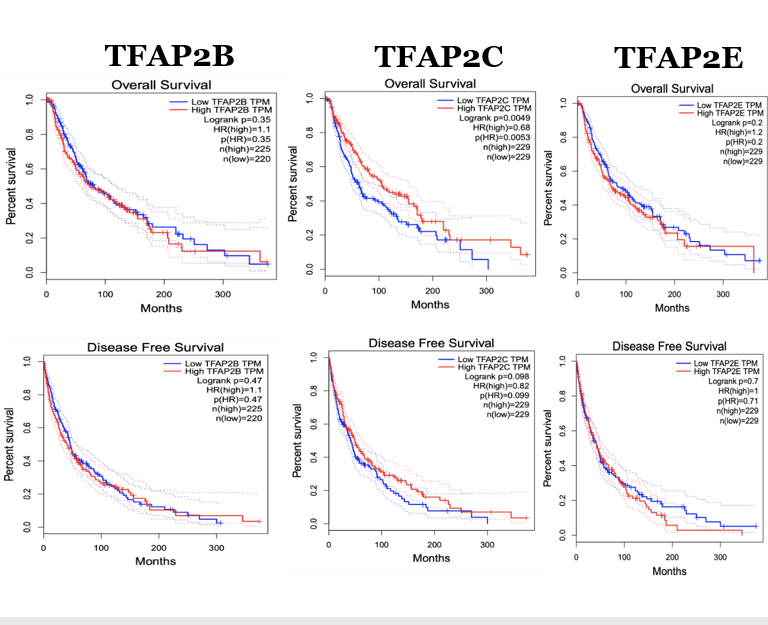
- Identified most important isoform to target based on the hazard rates.
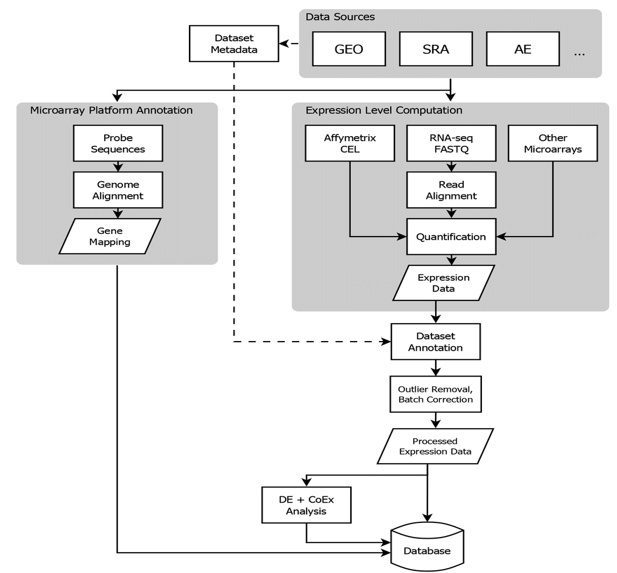
- Accessed the query dataset with ID GSE190610 for TFAP2 through the NCBI data gathering process via annotation, computation for implementation.
- Compared the wild type and TFAP2 knockout SkMel28 cell line data through bulk genomics techniques (RNAseq).
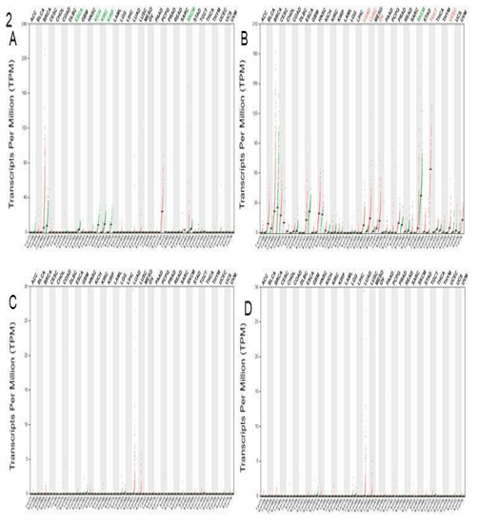
- Fetched a differentially expressed gene list between TFAP2 knockout SkMel28 vs wild type SkMel28 from the dataset.
- Considered Fold change (a change in measured value of expression) with -3 or more as down-regulated genes and those were selected for further analysis and usage in the implementation process.
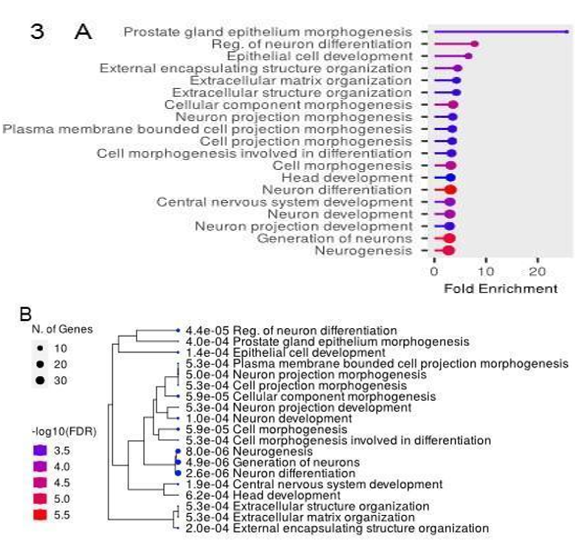
- Performed Gene ontology analysis to down regulated genes to assess the effect of TFAP2 knockout.
TFAP2 Isoforms Analysis
Data Representation
Gene Ontology Analysis
NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus
Design
STEP 1: Designing of CRISPR RNA
- CRISPick server from Broad Institute is utilized for designing guide RNA.
- Two sgRNA with NGG PAM sequence for SpyoCas9 are selected to knock out the TFAP2A gene.
- Two based on their on-target and off-target score are chosen rom the given guide RNA sequences. One on the plus strand, the other one on the minus strand.
- The two sgRNA are
sgRNA
Strand
Efficacy Score
STEP 2: Preparation & Delivery of LNP Constructs
- The sgRNAs delivered in the form of RNP complex using LNP.
- The Cas9 prepared using thermo stable Cas9 derived site-directed mutagenesis mediated evolved iGeoCas9, an alternate Cas9 to increase specificity.
- For in vivo and therapeutic usage, GMP grade LNP is produced.
- LNP mediated co-delivery of iGeoCas9 RNPs is personalized as per the metastatic nature of the cancer.
- The delivery method using the LNP method is optimized based on collection.
Conclusion
- TFAP2 gene is differentially over expressed in melanoma compared to normal.
- Targeting TFAP2 gene can lead to poor innervation in melanoma.
- The CRISPR construct along with the gRNA target with LNP’s surface can be transported modified with ligands or antibodies that recognize and bind to specific markers or receptors uniquely expressed on cancer cells.
- This targeted binding increases the likelihood of preferential uptake by cancer cells while reducing uptake by healthy cells in the TME.